Cold Weather Hydroponics
Even when growing indoors as the temperature drops, you must keep an eye on your Grow Room to keep your plants happy and healthy. This guide to cold weather hydroponics gives you everything you need to grow in less than optimum conditions.
How to Keep your Grow Room Warm in Cold Weather
Insulation
A well-insulated grown room is fundamental for cold weather hydroponics. It helps to maintain the temperature of the plants. Pay attention to how cold the room you propose to use gets at night, when the temperature drops. Put a rug on the floor as a form of insulation. If the room you are converting has heating, all the better, use it to your advantage!
Lighting
Indoor HID lighting produces a lot of heat. Use this to your advantage for cold weather hydroponics, like in winter. Run your’ lights on‘ period at night when temperatures are lower. If your plants are in Veg when winter begins, consider increasing the ‘lights on‘ period from 18 – 24 hours.
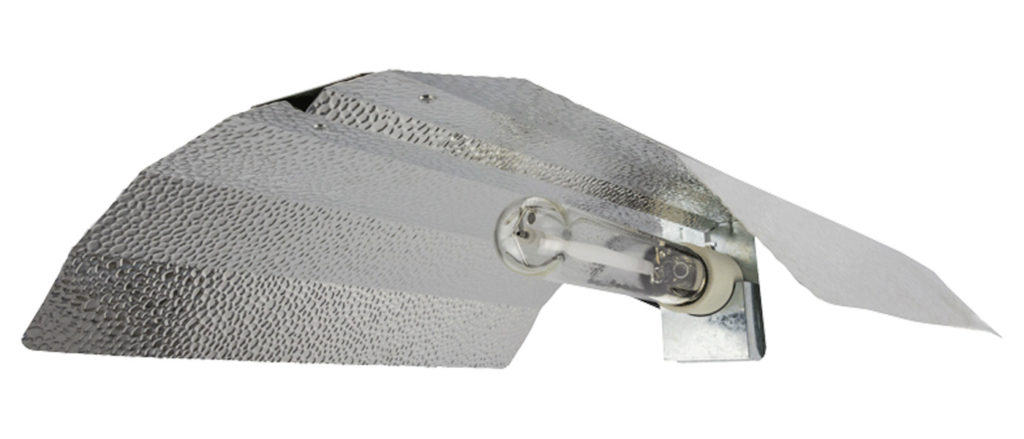

LED lighting can cause the opposite problem as they do not produce much heat. A simple solution is a grow room heater paired with a thermostat to keep a steady temperature. However, a heater could dry the air out, so invest in a humidistat to set your humidifier levels whilst the heater is on.
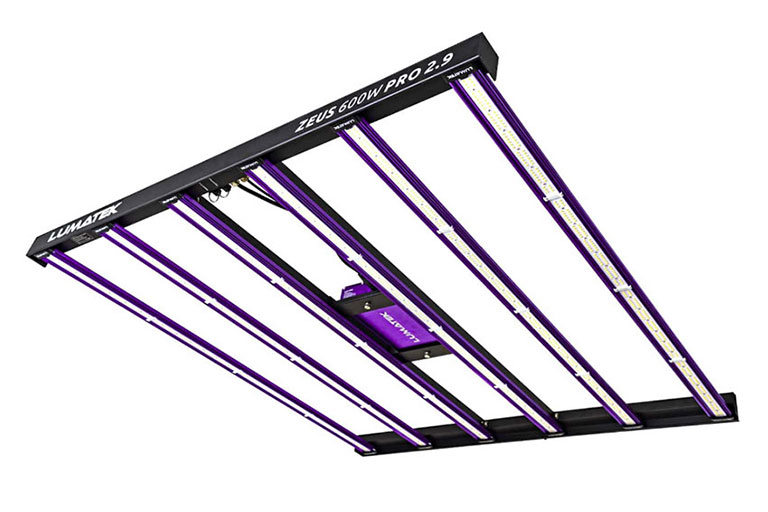

Cold Weather Hydroponics – Additional Heating
Tube Heaters are versatile enough to fit in most growing spaces. They emit a consistent heat spread and have a low running cost.

Tube Heaters are not thermostatically controlled. If you want this option, you could try using Oil Filled Radiators. They are a compact yet powerful way to reach optimum temperatures.
Fan Heaters are also an option for cold weather hydroponics. However, the dry, hot air expelled can lower humidity, damage plants and stunt growth if left blowing directly at them. For this reason, only use a fan heater outside the grow room to warm up the surrounding air or point towards the intake fan.
Nutrients
When mixing and storing nutrients in a water tank (reservoir) the temperature must be between 18-21°C. If it drops too low, it can slow down absorption and impede growth. If the solution gets too warm, oxygen levels will decrease, making plants more susceptible to diseases like Pythium. For
cold weather hydroponics, using a water heater, that sits in the water tank, helps to keep your pre-mixed nutrient solutions at the perfect temperature.

Intake Fan
Ensure that your intake fan is drawing air from an indoor source. Air drawn from inside will be warmer and contain more CO2. During vegetative growth and early bloom, turn the fan down by a few per cent to allow the warm air to circulate in the room for longer. If you are in mid to late Flower; however, unwanted odours might require the extraction fan to be on full. In this case, secondary heating will be needed to be considered.
Monitor Temperature
Plants like the air to be warm, thriving in temperatures between 25-28°C during “lights on” and around 18-21°C during “lights off”. This is important when growing in a Hydro system. Unlike soil or coco coir substrate, water offers little insulation. A Digital Thermometer is the best way to monitor the temperature.
Plant Growth And Cold Temperatures
Plants can sense when winter is coming. As temperatures start to fall, we see plant growth slowing down. Temperatures below 18°C will see a significant reduction in plant growth. Anything below 15°C could see your plant go into shock and halt all growth. If this happens, it can take 2-3 weeks for your plants to return to normal. There is also the risk that your plant will not recover at all.
What Happens When Plants Go into Shock?
When a plant goes into shock, it senses an attack on its roots. An extreme change in temperature is just the kind of threat that could help put the plant into shock. In response to the cold, the plant effectively shuts down. It stops all growth and focuses energy on protecting itself and repairing the roots, the plant’s lifeline. It will remain dormant until the threat it faces, i.e. the cold has gone.
As a last resort, you can use liquid heat products to fool plants into thinking the temperature is warmer than it is.
What to Do if Your Plants are Exposed to Cold
Bring the plant into a warm place, under grow lights or a propagator. Do not expose it to extreme heat conditions as this will worsen things. Just gentle warmth is needed. Some more ideas:
- Gently Clean the leaves so the plant can absorb more light.
- Trim any dead or dying foliage so that your plant does not waste energy trying to fix them.
- Only water when needed. When you do, use room temperature water.
- Keep a lookout for signs of mould, fungus, or bugs.
- If you need to re-pot, be very gentle. Roots are delicate as it is.
- Check if the roots are rotten. If the roots are brown and mushy, carefully trim them off as they are not making a comeback. Also use an enzyme. Enzymes digests decaying plant matter to recycle as food and prevent diseases.
Symptoms of Cold Weather Hydroponics – Shocked Plants
Depending on the extent of exposure, it may take 1-2 weeks for the entire damage to become visible.
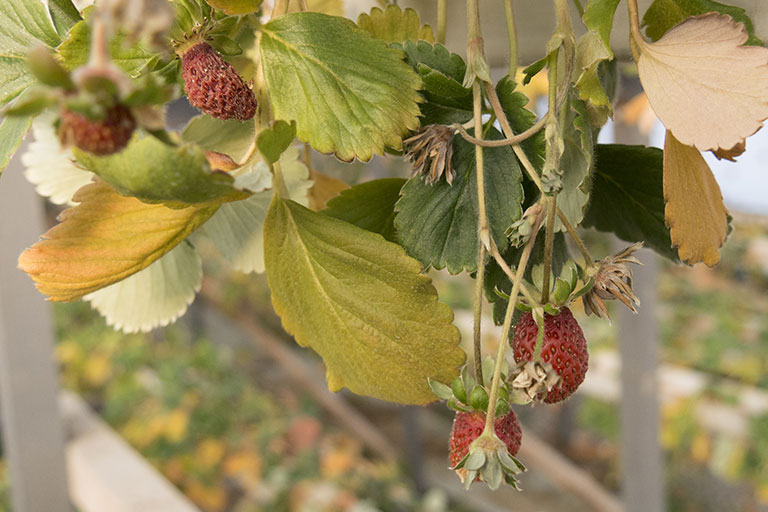

Cold damage may show as several of the following:
- Wilting or drooping leaves or small branches
- Softened or blackened foliage
- Burn-like spots on flowers and foliage
- Splits in woody stems or trunks
- Excessively loose root balls
Once the cold is no longer a threat, prune damaged leaves, shoots, and branches.